Answer:
A. 0.8 m/s to the right
Step-by-step explanation:
To find the momentum of the second astronaut, we need the momentum of the first one.
The momentum of astronaut 1, we will call it
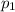 , is equal to mass * velocity:
, is equal to mass * velocity:
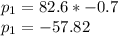
The momentum is negative since the left direction is considered negative.
Use the formula
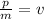 to find velocity:
to find velocity:
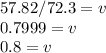
The astronaut must be moving to the right, since the first astronaut gave an impulse to the other astronaut to the right, therefore: 0.8m/s to the right.