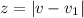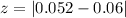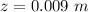Answer:
The distance is
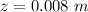
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The focal length is
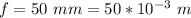
Generally the lens equation is mathematically represented as
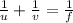
At image distance u = 1.5 m
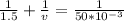
=>

=>
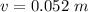
At image distance
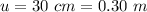
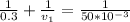
=>
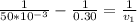
=>
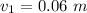
The distance the lens need to move is evaluate as