Answer:
The amount of heat that must be added to raise the temperature of 1.90 mol of air from 18.0 ° C to 37.0 ° C at constant volume is 749. 9775 J
Step-by-step explanation:
The properties cv and cp are called specific heats (or heat capacities) because, under certain special conditions, they relate the change in temperature of a system to the amount of energy added by heat transfer. Its SI units are
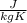 or
or
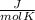 . Two specific heats are defined for gases, one for constant volume (cv) and the other for constant pressure (cp).
. Two specific heats are defined for gases, one for constant volume (cv) and the other for constant pressure (cp).
In the case of constant volume heating, the amount of heat entering the gas is equal to
Q=Cv*n*(Tfinal - Tinitial)
In this case:
- Air, being considered a diatomic gas, will have a molar heat capacity of:
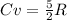 where R is the general gas constant, whose value in this case will be
where R is the general gas constant, whose value in this case will be
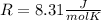
- n=1.90 mol
- Tfinal= 37 °C
- Tinitial= 18 °C
Replacing:
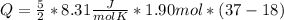
Taking into account that the difference in degrees kelvin is equal to the difference in degrees Celsius, and solving you get:
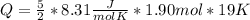
Q= 749. 9775 J
The amount of heat that must be added to raise the temperature of 1.90 mol of air from 18.0 ° C to 37.0 ° C at constant volume is 749. 9775 J