Answer:
The temperature at which the vapor pressure would be 0.350 atm is 201.37°C
Step-by-step explanation:
The relationship between variables in equilibrium between phases of one component system e.g liquid and vapor, solid and vapor , solid and liquid can be obtained from a thermodynamic relationship called Clapeyron equation.
Clausius- Clapeyron Equation can be put in a more convenient form applicable to vaporization and sublimation equilibria in which one of the two phases is gaseous.
The equation for Clausius- Clapeyron Equation can be expressed as:
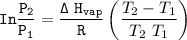
where ;
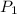 is the vapor pressure at temperature 1
is the vapor pressure at temperature 1
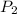 is the vapor pressure at temperature 2
is the vapor pressure at temperature 2
∆Hvap = enthalpy of vaporization
R = universal gas constant
Given that:
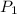 = 1 atm
= 1 atm
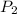 = 0.350 atm
= 0.350 atm
∆Hvap = 28.5 kJ/mol = 28.5 × 10³ J/mol
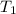 = 282 °C = (282 + 273) K = 555 K
= 282 °C = (282 + 273) K = 555 K
R = 8.314 J/mol/k
Substituting the above values into the Clausius - Clapeyron equation, we have:
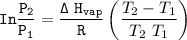
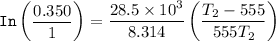
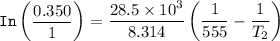
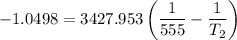
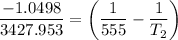
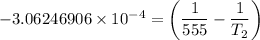
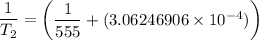
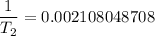
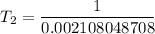
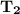 = 474.37 K
= 474.37 K
To °C ; we have
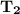 = (474.37 - 273)°C
= (474.37 - 273)°C
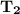 = 201.37 °C
= 201.37 °C
Thus, the temperature at which the vapor pressure would be 0.350 atm is 201.37 °C