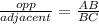Answer/Step-by-step explanation:
a. The sides of ∆ABC can be labelled as follows, taking θ as the reference point.
Adjacent = side AB
Opposite = side BC
Hypotenuse = side AC
b. I. "<B is an acute angle" => FALSE. It is a right angle (90°)
II. "The side opposite to <C is BC" => FALSE. The side opposite to <C is AB.
III. The side adjacent to <A is AB => TRUE
IV. The side opposite to <B is not the longest. => FALSE. It is the hypotenuse and the longest side.
c. Cos θ =
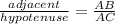
Tan θ =
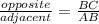
d. Sin C =
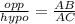
Cos C =
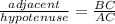
Tan C =