Answer: c = 4.97 and c = -1.97
Step-by-step explanation: Mean Value Theorem states if a function f(x) is continuous on interval [a,b] and differentiable on (a,b), there is at least one value c in the interval (a<c<b) such that:
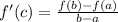
So, for the function f(x) =
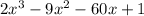 on interval [-4,9]
on interval [-4,9]
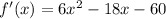
f(-4) =
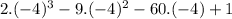
f(-4) = 113
f(9) =
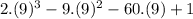
f(9) = 100
Calculating average:
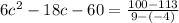
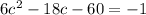
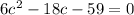
Resolving through Bhaskara:
c =
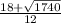
c =
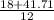 = 4.97
= 4.97
c =
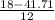 = -1.97
= -1.97
Both values of c exist inside the interval [-4,9], so both values are mean slope: c = 4.97 and c = -1.97