Answer:
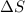 = 473.92J/K.mol
= 473.92J/K.mol
Step-by-step explanation: In physics, Entropy is defined as a degree of disorder in a system. Entropy change is given by the sum of all the products multiplied by their respective coeficients minus the sum of all the reagents multiplied by their respective coeficients:
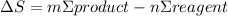
The balanced reaction:
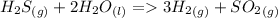
gives the proportion reagents react to form products, so, if 1.6 moles of
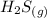 :
:
3.2 moles of water is used;
4.8 moles of hydrogen gas is formed;
1.6 moles of sulfur dioxide is also formed;
Calculating entropy change:
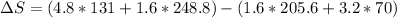
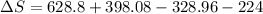
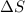 = 473.92J/K.mol
= 473.92J/K.mol
Entropy change for the given chemical reaction is
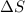 = 473.92J/K.mol
= 473.92J/K.mol