Answer:
The projectile strikes the tower at a height of 354.824 meters.
Step-by-step explanation:
The projectile experiments a parabolic motion, which consist of a horizontal motion at constant speed and a vertical uniformly accelerated motion due to gravity. The equations of motion are, respectively:
Horizontal motion
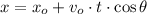
Vertical motion

Where:
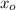 ,
,
 - Initial and current horizontal position, measured in meters.
- Initial and current horizontal position, measured in meters.
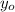 ,
,
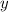 - Initial and current vertical position, measured in meters.
- Initial and current vertical position, measured in meters.
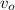 - Initial speed, measured in meters per second.
- Initial speed, measured in meters per second.
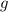 - Gravitational acceleration, measured in meters per square second.
- Gravitational acceleration, measured in meters per square second.
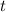 - Time, measured in seconds.
- Time, measured in seconds.
The time spent for the projectile to strike the tower is obtained from first equation:

If
 ,
,
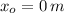 ,
,
 and
and
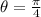 , then:
, then:


Now, the height at which the projectile strikes the tower is: (
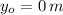 ,
,
 ,
,
 and
and
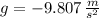 )
)


The projectile strikes the tower at a height of 354.824 meters.