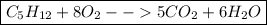Answer:
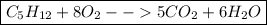
Step-by-step explanation:
Part 1: Count the number of atoms on each side per element
To start, count the number of atoms per element on both sides of the equation.
Left Side
C - 5 atoms
H - 12 atoms
O - 2 atoms
Right Side
C - 1 atom
H - 2 atoms
O - 3 atoms
Part 2: Balance carbon atoms
Now, with this information, you can begin finding out how to properly balance both sides of the equation.
You need 5 carbon atoms on the left, so place a coefficient of 5 in front of the
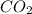 product. This will balance the carbons. Do not place a coefficient in front of the
product. This will balance the carbons. Do not place a coefficient in front of the
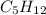 reactant - none are necessary!
reactant - none are necessary!
Then, you can update your counts for your atoms.
Left Side
C - 5 atoms
H - 12 atoms
O - 2 atoms
Right Side
C - 5 atoms
H - 2 atoms
O - 11 atoms
The updated equation will look like this:
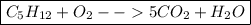
Part 3: Balance hydrogen atoms
Now, balance the hydrogen atoms. Place a coefficient of 6 in front of the
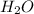 product. This will balance the hydrogen atoms.
product. This will balance the hydrogen atoms.
Once again, update the atom counts:
Left Side
C - 5 atoms
H - 12 atoms
O - 2 atoms
Right Side
C - 5 atoms
H - 12 atoms
O - 16 atoms
The updated equation will look like this:

Part 4: Balance oxygen atoms
To fully balance the equation, place a coefficient of 8 in front of the
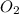 reactant. This will equalize the amount of oxygen atoms on both sides of the equation.
reactant. This will equalize the amount of oxygen atoms on both sides of the equation.
The updated equation will look like this:
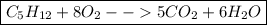
Part 5: Check the equation and atom counts
Now, update the atom counts one last time to make sure they are equal.
Left Side
C - 5 atoms
H - 12 atoms
O - 16 atoms
Right Side
C - 5 atoms
H - 12 atoms
O - 6 atoms
They are equal, so you may proceed.
Part 6: Check if reductions are necessary
If the equations coefficients can all be divided by a common divisor (i.e., 3), follow up with that step. However, any equation that has a reactant or product without a coefficient, skip this step entirely.
This equation falls into that category, so you may proceed past it.
Your final equation will look like this: