Answer:
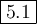
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Initial concentrations of reactants
[SO₂] = (3.8 mol)/(75 L) = 0.0507 mol·L⁻¹
[O₂] = (7.0 mol)/(75 L) = 0.0933 mol·L⁻¹
2. Equilibrium concentration of SO₃
[SO₃] = (1.5 mol)/(75 L) = 0.0200 mol·L⁻¹
3. Set up an ICE table
2SO₂ + O₂ ⇌ 2SO₃
I/mol·L⁻¹: 0.0507 0.0933 0
C/mol·L⁻¹: -2x -x +2x
E/mol·L⁻¹: 0.0507-2x 0.0933-x 2x
4. Calculate x
We know the final concentration of SO₃ is 0.0200 mol·L⁻¹, so
2x = 0.0200
x = 0.0100
5. Find the final concentrations of the reactants
Insert the numbers into the ICE table.
2SO₂ + O₂ ⇌ 2SO₃
I/mol·L⁻¹: 0.0507 0.0933 0
C/mol·L⁻¹: -0.0200 -0.0100 +0.0200
E/mol·L⁻¹: 0.0307 0.0833 0.0200
6. Calculate K
![K_{\text{eq}} = \frac{\text{[SO$_(3)$]}^(2)}{\text{[SO}_(2)]^(2)\text{[O$_(2)$]}} = (0.0200^(2))/(0.0307^(2)*0.0833) =\mathbf{5.1}\\\\\text{The value of the equilibrium constant is $\large \boxed{\mathbf{5.1}}$}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/bvndh61l0wktqnroh4t3gdyu4j1snwe6ur.png)