Answer: m = 0.42; Tb = 79°
Step-by-step explanation: The relationship between boiling point of the solvent above a solution is directly proportional to the molal concentration of the solute, i.e.:
ΔT =
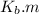
where
ΔT is the change in boiling point of the solvent;
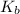 is the molal boiling point elevation constant;
is the molal boiling point elevation constant;
m is the molal concentration of the solute in the solution;
For there two solutions:
1) Ethanol:
ΔT =
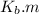
Tb -
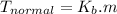
Tb - 78.4 = 1.22.m (1)
2) Carbon Tetrachloride:
Tb -
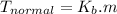
Tb - 76.8 = 5.03.m (2)
Solving the system of equations:
Tb - 78.4 = 1.22.m
Tb = 1.22.m + 78.4 (3)
Substituing (3) in (2)
1.22.m + 78.4 - 76.8 = 5.03m
3.81m = 1.6
m = 0.42
With m, find Tb:
T - 76.8 = 5.03.0.42
T = 2.11 + 76.8
T = 79°
Molal concentration is 0.42 and boiling point is 79°