Answer:
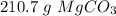
Step-by-step explanation:
We have to start with the reaction:
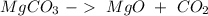
We have the same amount of atoms on both sides, so, we can continue. The next step is to find the number of moles that we have in the 110.0 g of carbon dioxide, to this, we have to know the atomic mass of each atom:
C: 12 g/mol
O: 16 g/mol
Mg: 23.3 g/mol
If we take into account the number of atoms in the formula, we can calculate the molar mass of carbon dioxide:
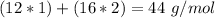
In other words:
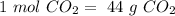 . With this in mind, we can calculate the moles:
. With this in mind, we can calculate the moles:
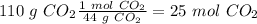
Now, the molar ratio between carbon dioxide and magnesium carbonate is 1:1, so:
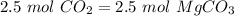
With the molar mass of
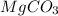 (
(
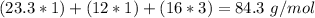 . With this in mind, we can calculate the grams of magnesium carbonate:
. With this in mind, we can calculate the grams of magnesium carbonate:
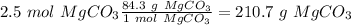
I hope it helps!