Answer:
E = 1.29*10^6N/C
Step-by-step explanation:
You take the cell membrane as a parallel plate capacitor. In order to calculate the magnitude of the electric field in between the membranes you use the following formula:
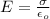 (1)
(1)
σ: surface charge density = 10^-5 C/m^2
εo: dielectric permittivity of vacuum = 8.85*10^-12C^2/Nm^2
You replace the values of the parameters in the equation (1):
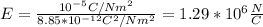
The magnitude of the electric field between the membrane cell is 1.29*10^6N/C