Answer:
a)
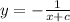
b) y = 0
Explanation:
Solution:-
- We are given a ODE of the form:
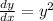
- To solve the given ODE and determine the general solution we will separate the variables in the given ODE as follows:
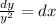
- Integrate both sides and determine a general explicit function of (y):
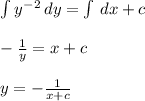
b) The singular solution that exist but is not included is the trivial solution corresponding to y = 0. This solution satisfies the the given ODE