Answer:
(a) 0.1585
(b) 0.4713
(c) 0.9545
Step-by-step explanation:
The random variable X can be defined as the number of heads.
The coin provided is balanced, i.e. P (H) = P (T) = 0.50
The outcome of tossing the coin are: (H and T). Each of these outcomes are independent of each other.
The random variable X thus follows a Binomial distribution with probability of success as 0.50.
For a large sample a Normal approximation to binomial can be applied to approximate the distribution of p if the following conditions are satisfied:
1. np ≥ 10
2. n(1 - p) ≥ 10
(a)
n = 100
Check the conditions as follows:
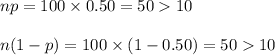
Thus, a Normal approximation to binomial can be applied.
So,
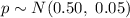
Compute the probability hat the proportion of heads will be anywhere from 0.49 to 0.51 as follows:
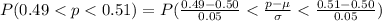

Thus, the probability hat the proportion of heads will be anywhere from 0.49 to 0.51 when a balanced coin is flipped 100 times is 0.1585.
(b)
n = 1000
Check the conditions as follows:
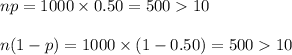
Thus, a Normal approximation to binomial can be applied.
So,
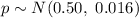
Compute the probability hat the proportion of heads will be anywhere from 0.49 to 0.51 as follows:
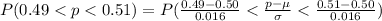

Thus, the probability hat the proportion of heads will be anywhere from 0.49 to 0.51 when a balanced coin is flipped 1000 times is 0.4713.
(c)
n = 10,000
Check the conditions as follows:
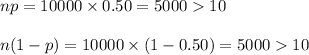
Thus, a Normal approximation to binomial can be applied.
So,
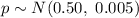
Compute the probability hat the proportion of heads will be anywhere from 0.49 to 0.51 as follows:
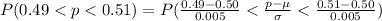

Thus, the probability hat the proportion of heads will be anywhere from 0.49 to 0.51 when a balanced coin is flipped 10,000 times is 0.9545.