Answer:
The test statistic to test the null hypothesis equals 1.059
Explanation:
From the given information; we have:
Treatment Observations
A 20 30 25 33
B 22 26 20 28
C 40 30 28 22
The objective is to find the test statistic to test the null hypothesis; in order to do that;we must first run through a series of some activities.
Let first compute the sum of the square;
Total sum of squares (TSS) = Treatment sum of squares
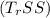 + Error sum of squares (ESS)
+ Error sum of squares (ESS)
where:
(TSS) =
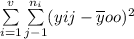 with (n-1) df
with (n-1) df
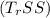
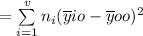 with (v-1) df
with (v-1) df
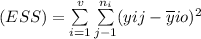 with (n-v) df
with (n-v) df
where;
v= 3
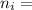 4
4
i = 1,2,3
n =12
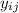 is the
is the
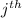 observation for the
observation for the
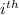 treatment
treatment
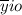 is the mean of the
is the mean of the
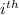 treatment i = 1,2,3 ; j = 1,2,3,4
treatment i = 1,2,3 ; j = 1,2,3,4
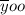 is the overall mean
is the overall mean
From the given data
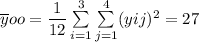
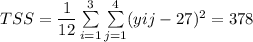
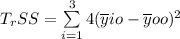
Total sum of squares (TSS) = Treatment sum of squares
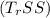 + Error sum of squares (ESS)
+ Error sum of squares (ESS)
(TSS) = 378 - 72
(TSS) = 306
Now; to the mean square between treatments (MSTR); we use the formula:
MSTR = TrSS/df(TrSS)
MSTR = 72/(3 - 1)
MSTR = 72/2
MSTR = 36
The mean square within treatments (MSE) is:
MSE = ESS/df(ESS)
MSE = 306/(12-3)
MSE = 306/(9)
MSE = 34
The test statistic to test the null hypothesis is :
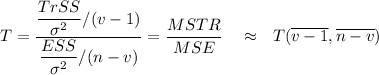
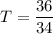
T = 1.059