Answer:
14 grams of calcium oxide would be produced by thermal decomposition of 25 grams of calcium carbonate.
Step-by-step explanation:
You know:
CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
In the first place, by stoichiometry of the reaction (that is, the relationship between the amount of reagents and products in a chemical reaction) the following quantities react and are produced:
- CaCO₃: 1 mole
- CaO: 1 mole
- CO₂: 1 mole
Being:
- Ca: 40 g/mole
- C: 12 g/mole
- O: 16 g/mole
the molar mass of the compounds participating in the reaction is:
- CaCO₃: 40 g/mole + 12 g/mole + 3*16 g/mole= 100 g/mole
- CaO: 40 g/mole + 16 g/mole= 56 g/mole
- CO₂: 12 g/mole + 2*16 g/mole= 44 g/mole
Then, by stoichiometry of the reaction, the following mass amounts of the compounds participating in the reaction react and are produced:
- CaCO₃: 1 mole* 100 g/mole= 100 g
- CaO: 1 mole* 56 g/mole= 56 g
- CO₂: 1 mole* 44 g/mole= 44 g
You can then apply the following rule of three: if by stoichiometry of the reaction 100 grams of calcium carbonate CaCO₃ produce 56 grams of calcium oxide CaO, 25 grams of CaCO₃ how much mass of CaO will it produce?
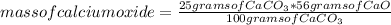
mass of calcium oxide= 14 grams
14 grams of calcium oxide would be produced by thermal decomposition of 25 grams of calcium carbonate.