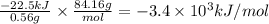Answer:
-3.4 × 10³ kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
Step 1: Calculate the heat absorbed by the calorimeter
We will use the following expression.
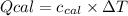
where,
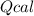 : heat absorbed by the calorimeter
: heat absorbed by the calorimeter
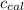 : heat capacity of the calorimeter
: heat capacity of the calorimeter
 : change in the temperature
: change in the temperature
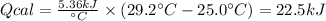
Step 2: Calculate the heat released by the combustion
According to the law of conservation of energy, the sum of the heat absorbed by the calorimeter and the heat released by the combustion is zero.
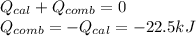
Step 3: Calculate the standard enthalpy of the combustion
22.5 kJ are released when 0.56 g of C₆H₁₂ (MW 84.16) is combusted. The standard enthalpy of the combustion (ΔH°c) is: