Answer:
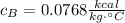
Step-by-step explanation:
In order to calculate the specific heat of the material B, you use the following formula for the change in the temperature of a substance, where an amount of heat Q is given to the substance:
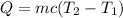
Q: amount oh heat
m: mass of the substance
T2: final temperature
T1: initial temperature
c: specific heat of the substance.
If QA and QB are the heat of material A and B, you have:
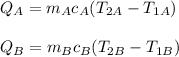
both materials have the same mass, mA = mB
cA: specific heat of A = 0.2007 kcal/(kg.°C)
cB: specific heat of B = ?
T2A: final temperature of A = 86.3°C
T1A: initial temperature of A = 22.0°C
T2B: final temperature of B = 190.0°C
T1B: initial temperature of B = 22.0°C
In this case you have that both material A and B receive the same amount of heat Q. Then, you equal QA with QB and solve for cB:
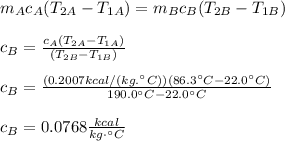
hence, the specific heat of the second rod B is 0.0768kcal/(kg°C)