Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
T₁ = 100 + 273 = 373K
T₂ = 273 + 119 = 392 K
V₁ = initial volume
V₂ = Final volume
P₁ = P₁
P₂ = .85P₁
Using gas law equation
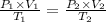
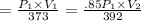
V₂ = 1.236 V₁
% increase in volume
= V₂-V₁ / V₁ x 100
= (1.236 V₁ - V₁ / V₁)x 100
= .236 x 100
= 23.6 % .