Answer:
a) H0: p1 - p2 = 0
H1: p1 - p2 ≠ 0
b) z=-0.58
c) p-value = 0.562
Explanation:
We need to determine whether p1 is not equals p2, so the null and alternative hypothesis are:
H0: p1 - p2 = 0
H1: p1 - p2 ≠ 0
Where p1 and p2 are the proportions of the population. Additionally, the proportions of the sample p1' and p2' are calculated as:
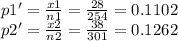
Then, the test statistic is calculated using the following equation:
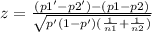
Where p' is calculated as:
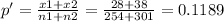
So, replacing the values, we get that the test statistic is:
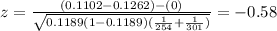
Finally, using the standard normal table, the p-value is equal to:
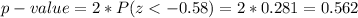
The p-value is greater that the value of alpha 0.1, so we can't reject the null hypothesis and there is evidence to said that p1 and p2 are equals.