Answer to A:
16.67%
Explanation to A:
If we need a number greater than five, the only number left is six, meaning there is
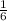
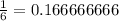
We can make it a percent by moving the decimal two places to the right and rounding to the thousandths place (two numbers). This would make our final answer 16.67%
Answer to B:
50%
Explanation to B:
There are three even numbers: 2, 4, and 6. This means we have a
 chance to land on one.
chance to land on one.
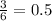
0.5 = 50%