Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Glucose + ATP → glucose 6-phosphate + ADP The equilibrium constant, Keq, is 7.8 x 102.
In the living E. coli cells,
[ATP] = 7.9 mM;
[ADP] = 1.04 mM,
[glucose] = 2 mM,
[glucose 6-phosphate] = 1 mM.
Determine if the reaction is at equilibrium. If the reaction is not at equilibrium, determine which side the reaction favors in living E. coli cells.
The reaction is given as
Glucose + ATP → glucose 6-phosphate + ADP
Now reaction quotient for given equation above is
![q=\frac{[\text {glucose 6-phosphate}][ADP]}{[Glucose][ATP]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/vua8awmydq1wbcrb4sv0e67m27x7ivx7va.png)
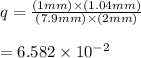
so,
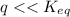 ⇒ following this criteria the reaction will go towards the right direction ( that is forward reaction is favorable until q = Keq
⇒ following this criteria the reaction will go towards the right direction ( that is forward reaction is favorable until q = Keq