Answer:
The probability of observing between 9 and 15 (inclusive) swarms is 0.6639.
Explanation:
The random variable X can be defined as the number of swarms of honeybees seen each spring.
The average value of the random variable X is, λ = 13.
A random variable representing the occurrence of events in a fixed interval of time is known as Poisson random variables.
For example, the number of customers visiting the bank in an hour or the number of typographical error is a book every 10 pages.
So, the random variable X follows a Poisson distribution with parameter λ = 13.
The probability mass function of X is as follows:
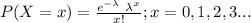
Compute the the probability of observing between 9 and 15 (inclusive) swarms as follows:
P (9 ≤ X ≤ 15) = P (X = 9) + P (X = 10) + P (X = 11) + ... + P (X = 15)
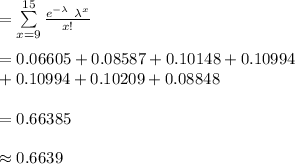
Thus, the probability of observing between 9 and 15 (inclusive) swarms is 0.6639.