1. Answer (D). By the law of sines, we have
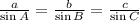 in any
in any
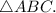
2. Answer (C). The law of cosines,
 accepts up to three sides and an angle as an input.
accepts up to three sides and an angle as an input.
3. Answer (D). Although this triangle is right, we are not given enough information to uniquely determine its sides and angles - here, we need either one more side or one more angle.
4. Answer (D). Don't get tripped up by answer choice (C) - this is just a rearrangement of the statement of the law of cosines. In choice (D), the signs of
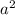 and
and
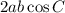 are reversed.
are reversed.
5. Answer (B). By the law of sines, we have
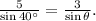 Solving gives
Solving gives
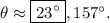 Note that this is the ambiguous (SSA) case of the law of sines, where the given measures could specify one triangle, two triangles, or none at all!
Note that this is the ambiguous (SSA) case of the law of sines, where the given measures could specify one triangle, two triangles, or none at all!
6. Answer (A). Since we know all three sides and none of the angles, starting with the law of sines will not help, so we begin with the law of cosines to find one angle; from there, we can use the law of sines to find the remaining angles.