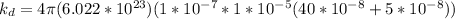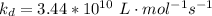Complete Question
The complete question is shown on the first uploaded image
Answer:
The rate constant is
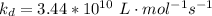
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The values for an enzyme is given as
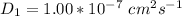
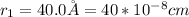
The values of a small molecular substrate is
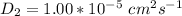
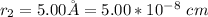
The equation relating the rate constant is
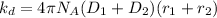
substituting values