Answer:
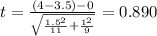
The p value for this case would be:
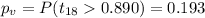
The p value is higher than the significance level so then we can conclude that we can FAIL to reject the null hypothesis and then the true mean for group A is not significantly higher than the mean for B
Step-by-step explanation:
Information given
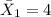 represent the mean for sample A
represent the mean for sample A
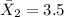 represent the mean for sample B
represent the mean for sample B
 represent the sample standard deviation for A
represent the sample standard deviation for A
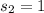 represent the sample standard deviation for B
represent the sample standard deviation for B
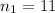 sample size for the group A
sample size for the group A
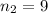 sample size for the group B
sample size for the group B
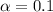 Significance level provided
Significance level provided
t would represent the statistic
Hypothesis to test
We want to verify if the student who graduates from college A has taken more math classes, on the average, the system of hypothesis would be:
Null hypothesis:
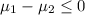
Alternative hypothesis:
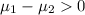
The statistic is given by:
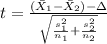 (1)
(1)
And the degrees of freedom are given by
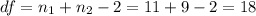
Replacing we got:
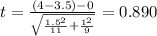
The p value for this case would be:
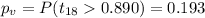
The p value is higher than the significance level so then we can conclude that we can FAIL to reject the null hypothesis and then the true mean for group A is not significantly higher than the mean for B