Answer:
Explanation:
Hello!
The variable of interest is:
X: motor skills of a sober subject.
n= 20
X[bar]= 37.1
S= 3.7
The claim is that the average score for all sober subjects is equal to 35.0, symbolically: μ= 35.0
The hypotheses are:
H₀: μ = 35.0
H₁: μ ≠ 35.0
α: 0.01
The statistic to use, assuming all conditions are met, is a one sample t- test
![t= (X[bar]-Mu)/((S)/(√(n) ) ) ~t_(n-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/vwi0rofs07t1yyn0s33gwf20ch4z9u7qtw.png)
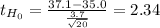
This test is two-tailed, meaning, the rejection region is divided in two and you'll reject the null hypothesis to low values of t or to high values of t:
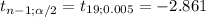
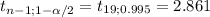
The decision rule using this approach is:
If
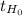 ≤ -2.861 or if
≤ -2.861 or if
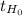 ≥ 2.861, you reject the null hypothesis.
≥ 2.861, you reject the null hypothesis.
If -2.861 <
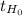 < 2.861, you do not reject the null hypothesis.
< 2.861, you do not reject the null hypothesis.
The value is within the non rejection region, the decision is to not reject the null hypothesis.
I hope this helps!