Complete Question
The complete question is shown on the first uploaded image
Answer:
a

b
![r = ( k [NO_2]^2 [F_2])/([NO_2F])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/agba0igkmgw78dx5e91z9b53a9c2fu9ckt.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The formation mechanism is
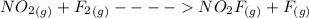
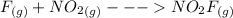
The overall balanced equation is

We combined the first reactant and the last product and the balanced the number of mole
The observable rate law is
![r = ( k [NO_2]^2 [F_2])/([NO_2F])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/agba0igkmgw78dx5e91z9b53a9c2fu9ckt.png)
This rate law is derived from the balanced chemical equation