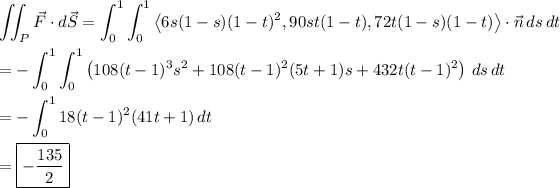The plane has intercepts
y = z = 0 ⇒ 3x = 6 ⇒ x = 2
x = z = 0 ⇒ 2y = 6 ⇒ y = 3
x = y = 0 ⇒ z = 6
and thus passes through the points (2, 0, 0), (0, 3, 0), and (0, 0, 6).
Parameterize the portion of the plane (call it P) by the vector function,
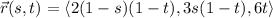
where 0 ≤ s ≤ 1 and 0 ≤ t ≤ 1.
Compute the normal vector to P :
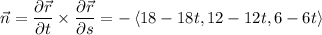
Then the flux of F through P is given by the surface integral,