This kind of problems becomes extremely easy if you use the consevation of energy. We know that, at any given moment, the total energy is constant.
Specifically, the energy is given by the sum of the kinetic and potential energy:
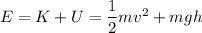
At the beginning, the egg has no velocity (
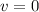 ), it's mass is 0.05, and its height is 2m, so the initial energy is
), it's mass is 0.05, and its height is 2m, so the initial energy is
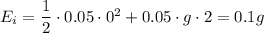
When the egg hits the ground, its height has become zero. So, the total energy is
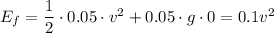
The initial and final energies must be the same, so we have
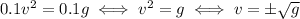
Discarding the negative solution, which woudln't make sense, we have
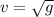
where
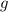 is the acceleration due to gravity
is the acceleration due to gravity