Answer:
The test statistic t is t=2.9037.
The null hypothesis is rejected.
For a significance level of 0.05, there is enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
Explanation:
The question is incomplete:
The sample 1, of size n1=25 has a mean of 1.15 and a standard deviation of 0.31.
The sample 2, of size n2=25 has a mean of 0.95 and a standard deviation of 0.15.
This is a hypothesis test for the difference between populations means.
The null and alternative hypothesis are:
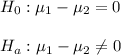
The significance level is α=0.05.
The difference between sample means is Md=0.2.
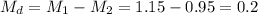
The estimated standard error of the difference between means is computed using the formula:
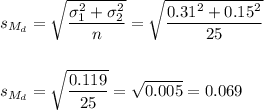
Then, we can calculate the t-statistic as:
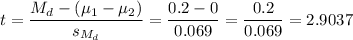
The degrees of freedom for this test are:
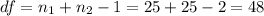
This test is a two-tailed test, with 48 degrees of freedom and t=2.9037, so the P-value for this test is calculated as (using a t-table):
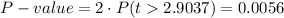
As the P-value (0.0056) is smaller than the significance level (0.05), the effect is significant.
The null hypothesis is rejected.