Answer:
3
Explanation:
If it's a right triangle, the Pythagorean theorem applies. Remember that is
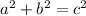
The longest side (c) will be x+2, and the other two sides are a and b.
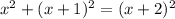
Now we have to solve this all out. :(
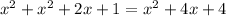
Combine like terms.
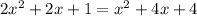
Move everything to one side, combining like terms.
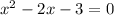
Now factor.
(x-3)(x+1) = 0
x = 3 or -1.
Clearly a side can't be -1 units, so the answer is 3.
You also can do this much faster if you remember the Pythagorean triple 3, 4, 5.