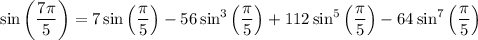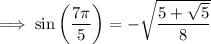I suppose you mean to find the value of the expression (not function) sin(14π/10).
To start, 14/10 = 7/5.
Next, expand sin(7x) using the angle sum identity,
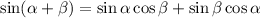
This lets us write
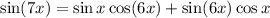
and we can keep applying the identity to the multiple-angle argument to wind up with
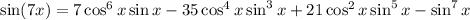
We can replace
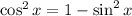 to write this in terms of sin(x) only.
to write this in terms of sin(x) only.
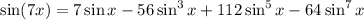
Then we can find the value of sin(7π/5) by plugging in π/5. But to do that, we need to first find the value of sin(π/5).
Using the same process as above, we have
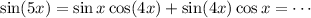
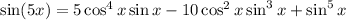
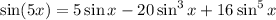
When x = π/5, the left side reduces to sin(π) = 0. Let y = sin(π/5). Then
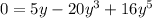
Factorize the right side:
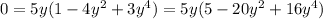
Solving for y tells us that either y = 0 (which can't be true, because 0 < π/5 < π/2 means 0 < sin(π/5) < 1), or
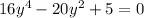
Using the quadratic formula, we find
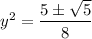
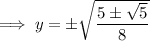
or 4 possible values, approximately -0.5878, 0.5878, -0.9512, or 0.9512.
Of course, only one of these values can be correct. We know sin(π/5) should be positive, so we throw out the two negative options. Also, sin(x) is strictly increasing over (0, π/2). This means 0 < π/5 < π/4 tells us 0 < sin(π/5) < sin(π/4), and sin(π/4) is approximately 0.707. Then sin(π/5) must be 0.5878, or exactly
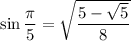
Now plug this into the identity we found for sin(7x).