The question is incomplete, here is the complete question:
What is the calculated value of the cell potential at 298 K for an electrochemical cell with the following reaction, when the H₂ pressure is 6.56 x 10⁻² atm, the H⁺ concentration is 1.39 M, and the Sn²⁺ concentration is 9.35 x 10⁻⁴ M?
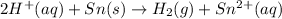
Answer: The cell potential of the given electrochemical cell is 0.273 V
Step-by-step explanation:
For the given chemical equation:
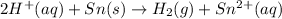
The half cell reactions for the given equation follows:
Oxidation half reaction:
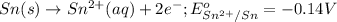
Reduction half reaction:
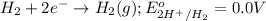
Oxidation reaction occurs at anode and reduction reaction occurs at cathode.
To calculate the
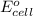 of the reaction, we use the equation:
of the reaction, we use the equation:
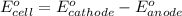
Putting values in above equation, we get:
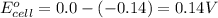
To calculate the EMF of the cell, we use the Nernst equation, which is:
![E_(cell)=E^o_(cell)-(0.059)/(n)\log ([Sn^(2+)]* p_(H_2))/([H^+]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/li47urxg6iy0u1ojlhml2rlmd40cuipnjo.png)
where,
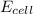 = electrode potential of the cell = ?
= electrode potential of the cell = ?
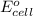 = standard electrode potential of the cell = +0.14 V
= standard electrode potential of the cell = +0.14 V
n = number of electrons exchanged = 2
![[H^(+)]=1.39M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/mzl80b3ykxb9q5pyxuswf1mp0kdqnktc47.png)
![[Sn^(2+)]=9.35* 10^(-4)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/z4ehpd413boxqpsr4zcn5r64vpcvg60fa2.png)
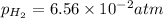
Putting values in above equation, we get:
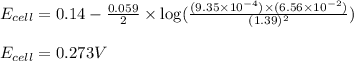
Hence, the cell potential of the given electrochemical cell is 0.273 V