Answer: The pH of the solution in the flask after the chemist has added 231.4 mL of NaOH solution to it is 12.018.
Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Molarity of NaOH = 0.32 M
Molarity of
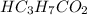 = 0.32 M,
= 0.32 M,
Volume of
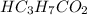 = 216.8 ml = 0.2168 L (as 1 L = 1000 mL)
= 216.8 ml = 0.2168 L (as 1 L = 1000 mL)
Volume of NaOH = 231.4 ml = 0.2314 L
Therefore, number of moles of
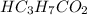 is as follows.
is as follows.
No. of moles = Molarity × Volume
=
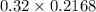
= 0.069 moles
Now, number of moles of NaOH will be calculated as follows.
No. of moles = Molarity × Volume
=
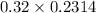
= 0.074 moles
Chemical equation for this reaction is as follows.
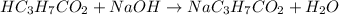
Initial: 0.069 0.074
Change: -0.069 -0.069
Equilibm: 0 0.004672
Total volume will be as follows.
0.2168 + 0.2314 = 0.4482 L
Here, the concentration of NaOH is equal to the concentration of hydroxide ions.
So, [NaOH] =
![[OH^(-)] = (n)/(V)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/6e67q150vlxnea7l4d3mx28ykez2hm65wl.png)
=
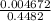
= 0.010424 M
We know that,
pOH =
![-log [OH^(-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/zv1af3ysn0xxbuqqoy4ytmwom7cppopfmk.png)
= -log (0.010424)
= 1.928
Hence, the pH will be calculated as follows.
pH = 14 - pOH
= 14 - 1.982
= 12.018
Thus, we can conclude that the pH of the solution in the flask after the chemist has added 231.4 mL of NaOH solution to it is 12.018.