Answer:

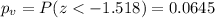
If we compare the p value and the significance level assumed
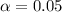 we have
we have
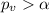 so we can conclude that we have enough evidence to FAIL to reject the null hypothesis, and we can said that at 5% of significance the proportion of defectives for robots is not significantly lower than the proportion of defectives for human
so we can conclude that we have enough evidence to FAIL to reject the null hypothesis, and we can said that at 5% of significance the proportion of defectives for robots is not significantly lower than the proportion of defectives for human
Explanation:
Data given and notation
n=490 represent the random sample taken
X=11 represent the number of defectives for robots
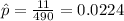 estimated proportion of defectives for robots
estimated proportion of defectives for robots
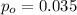 is the value that we want to test
is the value that we want to test
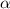 represent the significance level
represent the significance level
z would represent the statistic (variable of interest)
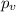 represent the p value (variable of interest)
represent the p value (variable of interest)
Concepts and formulas to use
We need to conduct a hypothesis in order to test the claim that the true proportion of defectives for robots is lower than for the humans :
Null hypothesis:
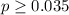
Alternative hypothesis:
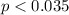
When we conduct a proportion test we need to use the z statistic, and the is given by:
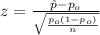 (1)
(1)
The One-Sample Proportion Test is used to assess whether a population proportion
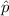 is significantly different from a hypothesized value
is significantly different from a hypothesized value
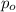 .
.
Calculate the statistic
Since we have all the info requires we can replace in formula (1) like this:

Statistical decision
It's important to refresh the p value method or p value approach . "This method is about determining "likely" or "unlikely" by determining the probability assuming the null hypothesis were true of observing a more extreme test statistic in the direction of the alternative hypothesis than the one observed". Or in other words is just a method to have an statistical decision to fail to reject or reject the null hypothesis.
The significance level assumed for this case is
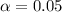 . The next step would be calculate the p value for this test.
. The next step would be calculate the p value for this test.
Since is a lower tail test test the p value would be:
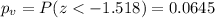
If we compare the p value and the significance level assumed
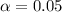 we have
we have
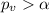 so we can conclude that we have enough evidence to FAIL to reject the null hypothesis, and we can said that at 5% of significance the proportion of defectives for robots is not significantly lower than the proportion of defectives for human
so we can conclude that we have enough evidence to FAIL to reject the null hypothesis, and we can said that at 5% of significance the proportion of defectives for robots is not significantly lower than the proportion of defectives for human