Answer:
(a).
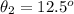
(b).
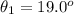
Step-by-step explanation:
(a).
Snell's law says
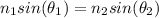
which in our case gives
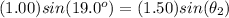
Solving for
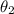 gives
gives
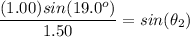
![\theta_2 = sin^(-1)[((1.00)sin(19.0^o))/(1.50)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/middle-school/b57bmys69gh61f9k2e4gqhstzpcosdnqzx.png)
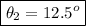
which is the angle of refraction from air to glass.
(b).
When the light ray goes from glass to back to air again, the angle of refraction equals the angle with which it had entered the glass because of the symmetry in Snell's law:
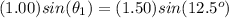
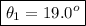
The result is that the outgoing ray (one that refracted out from glass to air) and the tracing of the incoming ray (one that refracted into the glass) are parallel to each other.