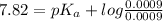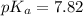Complete Question
You determine that it takes 26.0 mL of base to neutralize a sample of your unknown acid solution. The pH of the solution was 7.82 when exactly 13 mL of base had been added, you notice that the concentration of the unknown acid was 0.1 M. What is the pKa of your unknown acid?
Answer:
The pK_a value is
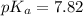
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told
The volume of base is
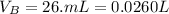
The pH of solution is
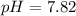
The concentration of the acid is
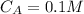
From the pH we can see that the titration is between a strong base and a weak acid
Let assume that the the volume of acid is
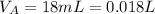
Generally the concentration of base
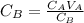
Substituting value
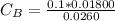
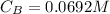
When 13mL of the base is added a buffer is formed
The chemical equation of the reaction is

Now before the reaction the number of mole of base is
![No \ of \ moles[N_B] = C_B * V_B](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/gezwf1jckqprc5uxdg6c1vl94ne7fzaln6.png)
Substituting value
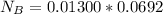
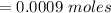
Now before the reaction the number of mole of acid is
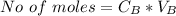
Substituting value
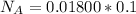
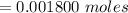
Now after the reaction the number of moles of base is zero i.e has been used up
this mathematically represented as
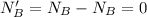
The number of moles of acid is
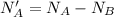
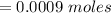
The pH of this reaction can be mathematically represented as
![pH = pK_a + log ([base])/([acid])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/rfcxj5yiswj1260zizhbw6kxr8oei3jsbw.png)
Substituting values