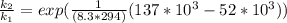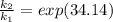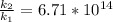Answer:
The factor by which the rate constant increases is
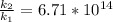
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The activation energy of oil before addition of Oil Spill Easter
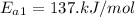
The activation energy of oil after addition of Oil Spill Easter
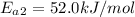
The temperature is
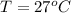
The objective of this solution is to obtain the factor by which the rate constant increase at 27°C
This can be obtained using the Arrhenius equation
This equation is mathematically represented as
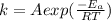
Where A is the frequency
k is the rate constant
R is the gas constant
This Arrhenius equation show a relationship between rate of reaction and
Activation energy
The decomposition of oil without catalyst is expressed as
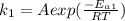
The decomposition of oil with catalyst is expressed as
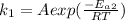
Now dividing
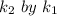
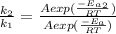
applying rule of exponent
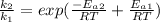
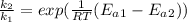
Substituting value