Answer:
 (Absolute minimum) and
(Absolute minimum) and
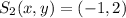 (Absolute maximum)
(Absolute maximum)
Explanation:
The critical points are determined with the help of the First Derivative Test:
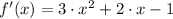
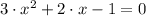
The critical points are:
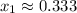 and
and
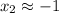
The Second Derivative Test offers a criterion to decide whether critical point is an absolute maximum and whether is an absolute minimum:
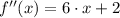
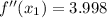 (Absolute minimum)
(Absolute minimum)
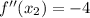 (Absolute maximum)
(Absolute maximum)
The critical points are:
 (Absolute minimum) and
(Absolute minimum) and
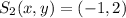 (Absolute maximum)
(Absolute maximum)