Answer:
The test statistic
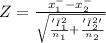
Explanation:
Explanation:-
Let x₁⁻ be the mean of the sample of size n₁ from a population mean μ₁ and standard deviation 'σ₁
Let x₂⁻ be the mean of the sample of size n₂ from a population mean μ₂ and standard deviation 'σ₂'
Null hypothesis : H0:μ₁ = μ₂
Alternative hypothesis : H1:μ₁ ≠μ₂
To test whether there is any significant difference between x₁⁻ and x₂⁻ we have use test statistic
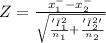
Here
- x₁⁻ be the mean of the first sample
- x₂⁻ be the mean of the second sample
- 'σ₁' be standard deviation first population.
- 'σ₂' be standard deviation second population.