Answer:
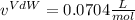
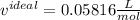
Differences:
- The gas is at a very high pressure, which causes strong nonidealities.
- Attraction and repulsion actually phenomena exist among molecules, which is not considered by the ideal gas equation.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, the VdW equation takes the typical form:
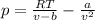
Whereas
 and
and
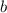 are referred to the attraction and repulsion effect, in such a way, for neon, such values are 0.208 bar*L²/mol² and 0.01672 L/mol respectively. However, with the given information, the polynomic form of the VdW equation is:
are referred to the attraction and repulsion effect, in such a way, for neon, such values are 0.208 bar*L²/mol² and 0.01672 L/mol respectively. However, with the given information, the polynomic form of the VdW equation is:
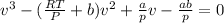
Which in terms of the molar volume becomes:
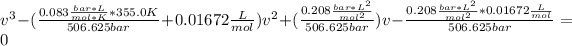
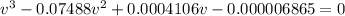
Thus, by solving via solver the roots, two are imaginary and the feasible molar volume is:
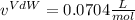
Now, the volume obtained from the ideal gas equation is:
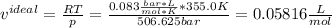
In this case, the two values are different because:
- The gas is at a very high pressure, which causes strong nonidealities.
- Attraction and repulsion actually phenomena exist among molecules, which is not considered by the ideal gas equation.
Best regards.