Answer:
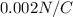
Step-by-step explanation:
Parameters given:
Charge of object, q = 5 mC =
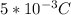
Acceleration of object, a =
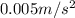
Mass of object, m = 2.0 g
The Electric field exerts a particular force on the object, causing it to accelerate (Electrostatic force).
We know that Electrostatic force, F, is given in terms of Electric field, E, as:
F = qE
This means that the object exerts a force of -qE on the Electric force (Action with equal and opposite reaction).
The object also has a force, F, due to its acceleration a. This force is the product of its mass and acceleration. Mathematically:
F = ma
Equating the two forces of the object, we get:
-qE = ma
=>
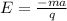
Solving for E, we have:
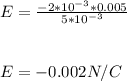
The magnitude will be:
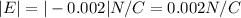
The electric field has a magnitude of 0.002 N/C.