Answer:
a) Parameters :-
The statistical constants of the population namely mean 'μ' and variance σ²
are referred to as parameters.
b Statistics:-
The statistical computed from sample observations mean (x⁻) and variance
(S² ) are usually referred as statistics
c) the test statistic
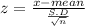
Explanation:
Explanation:-
Population:-
Population consists of the totality of the observations with which we are concerned. This number is finite or infinite.
The number of observations in the population is defined to be the size of the population.
Sample:-
A sample is a subset of a population
Parameters :-
The statistical constants of the population namely mean 'μ' and variance σ²
are referred to as parameters.
Statistics:-
The statistical computed from sample observations mean (x⁻) and variance
(S² ) are usually referred as statistics
Central limit theorem:
If x⁻ is the mean of a random sample of size n taken from a population with mean 'μ' and finite variance σ² , then the limiting form of the distribution
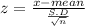
Z- distribution:-
Suppose we want to test whether the given sample of size n has been drawn from a population with mean ''μ'
we set up null hypothesis that there is no significance between sample mean x⁻ and mean 'μ ' then The test statistic
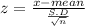
standard deviation of the population parameter σ and sample statistic mean x⁻
Z- distribution for the given single proportion
Suppose we want to test whether the given sample of size n has been drawn from a normal population.
we set up null hypothesis that there is no significance between sample proportion 'p' and Population proportion 'P' then The test statistic
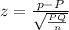
Q =1-P