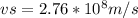Answer:
the observer can conclude that the object is moving with a radial velocity of
Step-by-step explanation:
In relation to Doppler effect for light, the formula can be represented as:
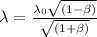
where,
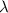 = wavelength of the light emitted by an object = 607.5 nm
= wavelength of the light emitted by an object = 607.5 nm
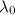 = wavelength of ultraviolet Lyman-alpha line of hydrogen by astronomical object = 121.5 nm
= wavelength of ultraviolet Lyman-alpha line of hydrogen by astronomical object = 121.5 nm
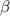 =
=
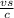
It is clear that the 'positive sign usually denotes "approaching" and the 'negative sign usually denotes "receding".
However, Since the object and the source are receding. Then, we have :
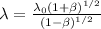
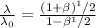
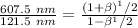
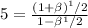
Squaring on both sides & we have:
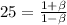
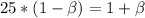
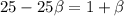
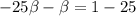
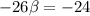
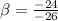
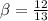
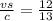
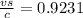
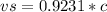

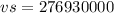
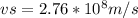
Therefore; the observer can conclude that the object is moving with a radial velocity of