Answer:
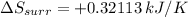
Step-by-step explanation:
Given: Entropy of surrounding: ΔSsurr = ?
Temperature: T= 355 K
The change in enthalpy of reaction: ΔH = -114 kJ
Pressure: P = constant
As we know, ΔH = -114 kJ ⇒ negative
Therefore, the given reaction is an exothermic reaction
Therefore, Entropy of surrounding at constant pressure is given by,
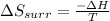
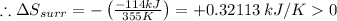
In the given reaction:
2NO(g) + O₂(g) → 2NO₂(g)
As, the number of moles of gaseous products is less than the number of moles of gaseous reactants.
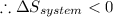
As we know, for a spontaneous process, that the total entropy should be positive.
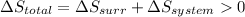
Therefore, at the given temperature,
- if
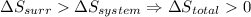 then the given reaction is spontaneous
then the given reaction is spontaneous
- if
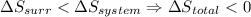 then the given reaction is non-spontaneous
then the given reaction is non-spontaneous