Answer: The kinetic energy of the ball when it is 0.26 m from its equilibrium position is 0 J.
Step-by-step explanation:
The ball is present in simple harmonic motion. During this motion, the speed of ball will be maximum at a distance from the equilibrium point.
We are given that the amplitude is 0.3 m and kinetic energy at x = 0.26 m will be calculated as follows.
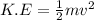
Here, v = 0
So,
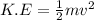
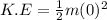
= 0 J
Thus, we can conclude that the kinetic energy of the ball when it is 0.26 m from its equilibrium position is 0 J.