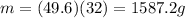Answer:
1587.2 g
Step-by-step explanation:
First of all, we need to calculate the number of moles of oxygen. We can do it by using the equation of state for an ideal gas:
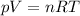
where in this case:
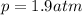 is the pressure of the gas
is the pressure of the gas
V = 640 L is the volume
n is the number of moles
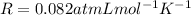 is the gas constant
is the gas constant
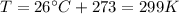 is the absolute temperature of the gas
is the absolute temperature of the gas
Solving for n, we find:
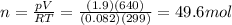
Now we can find the mass of the oxygen by using the formula:
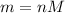
where:
n = 49.6 mol is the number of moles
M = 32 g/mol is the molar mass of molecular oxygen
Therefore, substituting,