Answer:
2.9 is the initial pH of the analyte solution.
Step-by-step explanation:
The dissociation constant of acetic acid as per theoretical value =
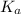
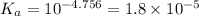
The initial concentration of acetic acid = c = 0.0900 M
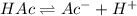
initially
c 0 0
At equilibrium
(c-x) x x
The expression of dissociation constant :
![K_a=([Ac^-][H^+])/([HAc])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/tlxc64l85qotpg0be6jo6z0ne52mtx8dcl.png)
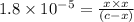
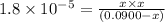
Solving for x:
x = 0.001264 M
![[H^+]=0.001264 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/o9cc3f0vkqp8s3iei7xxd1qncjsbf7eo82.png)
The pH of the solution :
![pH=-\log[0.001264]=2.898\approx 2.9](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/920tihh8b02gh7u07ruv7pnfvsh9g8o88b.png)
2.9 is the initial pH of the analyte solution.